Periodontal disease
Gum disease is one of the leading causes of tooth loss. Gum disease has two primary stages. If diagnosed and treated in the first stage, the condition can be reversed and tooth loss can usually be prevented. In order to prevent gum disease, practice good oral hygiene and visit your dentist for cleanings and check-ups twice a year.
If gum disease is detected during your visit, we will instruct you on steps regarding improved home care and recommend specialized treatment options in our office to eliminate the disease.
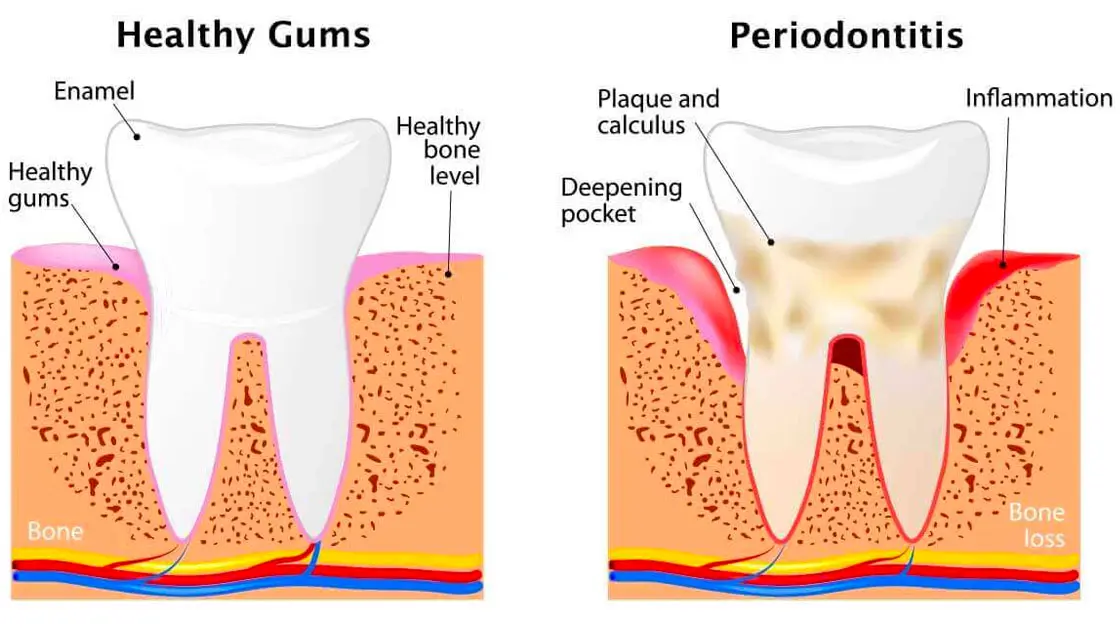
Gingivitis – early stage of gum disease
This stage only affects the soft tissue of the gums, and the patient may not experience any discomfort. Although the symptoms may be very mild, it is important to diagnose gum disease in this early stage before it progresses to periodontitis.
Symptoms of Gingivitis may include:
- Swollen or bleeding gums
- Bad breath or a metallic taste in the mouth
- Receding gums
- Increasing spaces between teeth
Periodontitis – advanced stages of gum disease
Periodontitis is the name for more advanced periodontal disease and if permitted to progress to this point, not only the gums are affected but the bone structures supporting the teeth will be compromised.
Without regular dental visits, symptoms may not be noticed until moderate periodontitis is present.